Have you ever wondered how scientists separate complex mixtures of substances? If so, you'll want to learn about paper chromatography, a separation technique that can help identify different components in a mixture. In this article, we'll dive into the principle behind paper chromatography, including how it works, what it's used for, and some practical applications in various scientific fields.
Chromatography is a method of separating different components of a mixture based on their physical and chemical properties. It is widely used in chemistry, biochemistry, and forensic science to identify and quantify various substances. Paper chromatography is one of the simplest forms of chromatography, which utilizes a special type of paper to separate the components of a mixture. The principle of paper chromatography is based on the fact that different substances have different affinities towards the paper and the solvent.
- History of Paper Chromatography
- Materials and Equipment Required for Paper Chromatography
- Principles of Paper Chromatography
- Procedure for Paper Chromatography
- Factors Affecting Paper Chromatography
- Applications of Paper Chromatography
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Paper Chromatography
- Types of paper chromatography
- FAQs
- Topics about paper chromatography
History of Paper Chromatography
The first paper chromatography experiment was performed by Mikhail Tsvet, a Russian botanist, in 1903. Tsvet used a special type of paper called adsorption paper, which was impregnated with calcium sulfate, to separate the components of plant pigments. Later, the technique was modified and improved by other scientists, including Archer John Porter Martin and Richard Laurence Millington Synge, who were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1952 for their work on partition chromatography, a type of chromatography related to paper chromatography.
Materials and Equipment Required for Paper Chromatography
The materials and equipment required for paper chromatography include:
- Chromatography paper (Whatman #1 or equivalent)
- Pencil or pen
- Ruler
- Scissors
- Sample applicator (capillary tube or micropipette)
- Solvent (e.g., water, ethanol, acetone, chloroform, etc.)
- Developing chamber (glass or plastic container with a lid)
- Filter paper
- UV lamp (optional)
Principles of Paper Chromatography
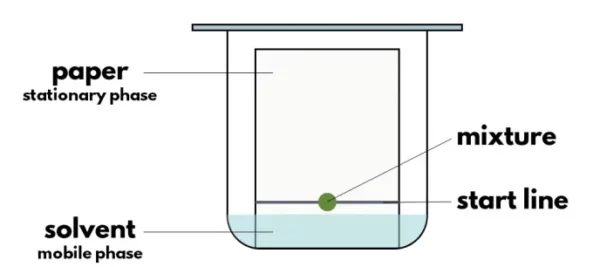
The principle of paper chromatography is based on the differential migration of substances through a stationary phase (paper) and a mobile phase (solvent). The paper used in paper chromatography is a thin, absorbent, and inert material that can be impregnated with different chemicals to improve its selectivity. The mobile phase is a liquid or gas that flows through the stationary phase by capillary action.
When a mixture is spotted on the paper, the different components of the mixture interact with the paper and the solvent differently, depending on their chemical and physical properties. The components that have a higher affinity towards the paper will move more slowly than the components that have a higher affinity towards the solvent. As a result, the components of the mixture will separate into different zones along the paper.
In paper chromatography, the adsorption chromatography or partition chromatography is involved in which components are divided or distributed between liquid phases. In this, a special chromatography paper is used in which water is trapped which is the stationary phase. A sample solution is spotted on the base of the page. In the appropriate solvent, the paper strip is suspended and the mobile phase rises through capillary action to the top of the paper. The analytes are selectively retained on the stationary phase (cellulose paper). The spots of different analytes move to different heights along the mobile phase and each component in the sample mixture separates based on varying degrees of adhesion.
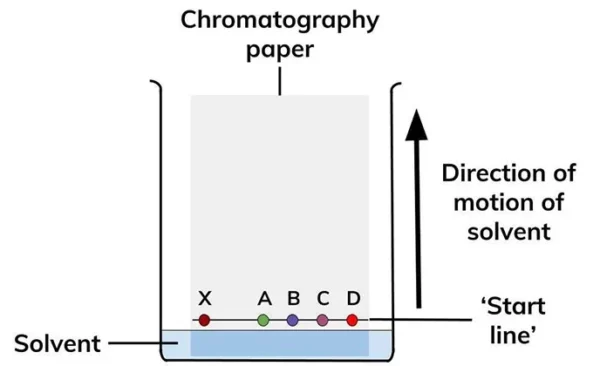
Procedure for Paper Chromatography
The procedure for paper chromatography involves the following steps:
- Cut a piece of chromatography paper to the desired size (usually 5-10 cm wide and 10-20 cm long).
- Draw a line with a pencil or pen about 1-2 cm from the bottom edge of the paper (the origin).
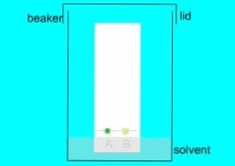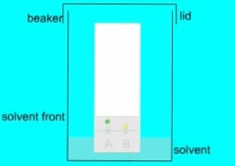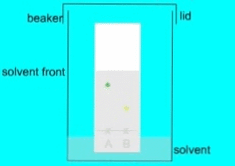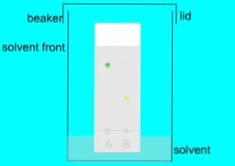
- Apply a small amount of the mixture to be separated at the origin using a sample applicator (capillary tube or micropipette).
- Place the paper in a developing chamber containing the solvent, making sure that the solvent level is below the origin line.
- Cover the developing chamber with a lid to prevent the solvent from evaporating and to ensure that the paper is saturated with the solvent.
- Allow the chromatogram to develop until the solvent front reaches the top of the paper or a desired distance.
- Remove the paper from the developing chamber and let it dry.
- Visualize the separated components by exposing the paper to a UV lamp or by using a staining agent such as iodine.
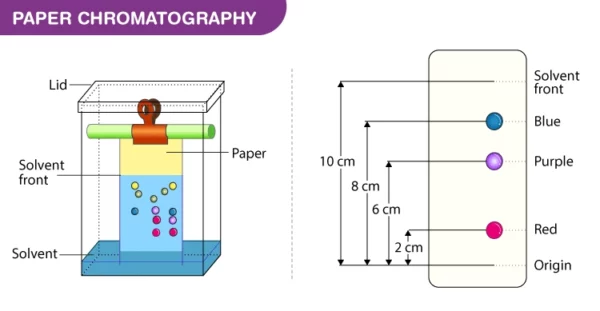
- Measure the distance traveled by each component from the origin and calculate the Rf (retention factor) value, which is a ratio of the distance traveled by the component to the distance traveled by the solvent.
Experimental Procedure of Paper Chromatography
- Choose an appropriate type of development: It’s decided based on the solvent, mixture, paper complexity, etc. As they are easy to execute, radial type or ascending paper chromatography is usually employed. It's also simple to handle, the chromatogram obtained is quicker.
- Selecting an appropriate filter paper: Based on a sample quality and pores size, the filter paper is selected.
- Sample preparation: Sample preparation involves dissolving the sample in an appropriate solvent that is used in the process of mobile phase making.
- Sample spot on paper: The sample mixture should be spotted in a proper position on the paper using a capillary tube.
- Development of chromatogram:The development of chromatograms is spotted by immersing the stationary phase (Paper) into the mobile phase. Because of the paper's capillary action, the mobile process passes over the paper sample.
- Paper drying and compound detection: Upon the development of the chromatogram, the paper is dried by an air dryer. Detecting solution also is sprayed on developed paper and dried to recognize the spots of the sample chromatogram. Paper with varying bands of analytes is observed under UV-light and further Rf values are calculated.
Factors Affecting Paper Chromatography
Several factors can affect the separation and resolution of the components in paper chromatography, including:
- The type and quality of the paper: Different types of paper have different porosity, thickness, and chemical composition, which can affect the retention and selectivity of the components.
- The type and concentration of the solvent: The solvent should have a high degree of purity and should be selected based on the polarity and solubility of the components.
- The temperature and humidity: High temperature and humidity can cause the solvent to evaporate quickly and can affect the reproducibility of the results.
- The amount and concentration of the sample: Too much sample can overload the paper and lead to poor resolution, while too little sample can result in weak signals.
-
Quality of paper used: Some papers are better absorbed and retained than the others. Have to try with the different types and brands of paper.
-
Length of the paper: Usually, separation will be better on long paper.
Type of Solvent used: The solubility of each compound have different, so for different effects of separation try the different solvent. -
The thickness of the paper: Paper thickness is difficult to travel the spot upwards.
The concentration of the sample or spot: the concentrated spot cannot separate properly and if the very diluted so It cannot be seen properly. -
Effect of Temperature: temperature can affect the separation of analytes.
Factors affecting Rf value in paper chromatography
Paper chromatography is a chromatographic method of separation in which the flow of solvent separates the substance by capillary action on the specially designed paper (cellulose filter paper) that acts as a stationary phase. The quantity of each analyte of the sample mixture can be determined using retention factors (Rf). Retention factors are helpful in the comparison between the chromatograms.Here are some factors that affect the Rf value of paper chromatography.
- The solvent system
- Composition of the mobile phase
- The working temperature of the system
- The quality of the paper used
- The distance through which the solvent runs
- The quality and nature of solvents used
- The polarity of components
- The pH of the solvent or mobile phase
- The thickness of the stationary phase
- Saturation or equilibrium of the mobile phase
- The concentration of the sample or spot
- Techniques applied for sample
Applications of Paper Chromatography
Paper chromatography has many applications in various fields, including:
- Biochemistry: It is used to separate and analyze amino acids, peptides, proteins, nucleotides, and other biomolecules.
- Forensic science: It is used to identify and compare ink, dyes, drugs, and other forensic samples.
- Food analysis: It is used to detect and quantify food additives, colorants, and flavors.
- Environmental monitoring: It is used to detect and quantify pollutants in water, soil, and air.
- Pharmaceutical analysis: It is used to analyze drug formulations, impurities, and degradation products.
- Paper chromatography is used for separating polar and non-polar compounds.
- It is used for the detection and separation of color mixtures including pigments as a qualitative analytical chemistry technique.
- Paper chromatography is used for identifying sugars, nucleic acids, lipids, amino acids, and other biomolecules.
- It is used in DNA/RNA sequencing.
- It is used to test pharmaceutical purity.
- It is used for the detection of pollutants in food and beverages.
- For investigations and criminal trials, paper chromatography is used in forensic research.
- This is used for ripening and fermentation study.
- It is used for the analysis of cosmetics.
- Paper chromatography is used for component separation and purification.
- Paper chromatography can be applied to monitor chemical synthesis reactions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Paper Chromatography
Some advantages of paper chromatography include:
- It is a simple and cost-effective method that does not require specialized equipment or training.
- It is a versatile technique that can be used to separate a wide range of substances.
- It is a rapid method that can yield results in a short time.
- Compounds are separated within a short time.
- Analysis of the paper chromatography required small sample quantities.
- It is an inexpensive technique compared to other chromatographic methods.
- It is possible to identify both organic and inorganic compounds.
- Paper chromatography is easy to use and setup.
Some disadvantages of paper chromatography include:
- It has a low resolution and sensitivity compared to other chromatographic techniques.
- It is prone to experimental errors and can be affected by the ambient conditions.
- It is a semi-quantitative method that requires calibration with standard samples.
- The use of paper chromatography techniques cannot separate volatile substances.
- Paper chromatography cannot separate large sample volumes.
- The paper chromatography has less accuracy compared to TLC, HPTLC, and HPLC.
- It is unable to separate the complex mixture.
- It cannot save results for long periods.
Advantages
- It requires fever quantitative material.
- Separation of compounds in a short time.
- Analysis requires a low amount of sample.
- Compare to other chromatography methods paper chromatography is a cheap technique.
- Organic as well as inorganic compounds can be identified by paper chromatography method.
- The setup of paper chromatography occupies less space than the other chromatographic method.
- Easy to handle and setup.
- The less sample quantity required for the analysis.
- Cost-effective method.
Disadvantages
- Volatile substances cannot be separated using paper chromatography techniques.
- Paper chromatography cannot be compatible with large amounts of sample.
- Quantitative analysis is not useful in paper chromatography.
- Paper chromatography cannot be separated complex mixture.
- As compared to the HPLC, TLC or HPTLC, paper chromatography has less accuracy.
- Data cannot be saved for long periods
Types of paper chromatography
- Ascending Paper Chromatography: As the name suggests the developing solvent or mobile phase travels in an upward direction
- Descending Paper Chromatography: In such paper chromatography, due to the gravitational pull and capillary action the direction of the solvent flow is downward
- Ascending-Descending Paper Chromatography: This type of paper chromatography the solvent first moves up on the paper folded over a rod and after crossing the rod it continues its path downwards.
- Horizontal or Circular Paper Chromatography: In this method, the sample mixture is employed in the center of a round paper placed on a flat surface.
- Two Dimensional Paper Chromatography: With the aid of two-dimensional paper chromatography, substances that have the same Rf values can be solved.
FAQs
-
What is paper chromatography used for? Paper chromatography is used for the separation and identification of various substances, including biomolecules, forensic samples, food additives, pollutants, and drugs.
-
What is the principle of paper chromatography? The principle of paper chromatography is based on the differential adsorption and migration of the components of a mixture through a porous medium, such as a sheet of filter paper. The components are separated based on their affinity to the stationary phase and the mobile phase, which can be a liquid or a gas.
-
How does paper chromatography work? Paper chromatography works by applying a small amount of the mixture to be separated at the origin of a special type of paper and placing the paper in a developing chamber containing a liquid or gas solvent. The solvent moves up the paper by capillary action, carrying the components of the mixture with it. The components are separated based on their affinity to the paper and the solvent, and their position on the paper can be visualized by exposing the paper to a UV lamp or a staining agent.
-
What are the advantages of paper chromatography? Some advantages of paper chromatography include its simplicity, low cost, versatility, and speed. It is a simple and cost-effective method that does not require specialized equipment or training. It is a versatile technique that can be used to separate a wide range of substances. It is a rapid method that can yield results in a short time.
-
What are the limitations of paper chromatography? Some limitations of paper chromatography include its low resolution and sensitivity compared to other chromatographic techniques, its susceptibility to experimental errors and ambient conditions, and its semi-quantitative nature that requires calibration with standard samples.
-
What are the factors affecting paper chromatography? Several factors can affect the separation and resolution of the components in paper chromatography, including the type and quality of the paper, the type and concentration of the solvent, the temperature and humidity, and the amount and concentration of the sample.
-
What is the basic principle of paper chromatography? The principle involved is partition chromatography in which the compounds are distributed or partitioned into liquid phases.
-
What is paper chromatography? Paper chromatography is a method of separating and identifying mixtures, especially pigments.
-
What is the major advantage of paper chromatography? The main advantages of paper chromatography are simplicity, rapid separation, low cost and have good sensitivity.
-
What type of paper is used in paper chromatography? Filter paper, chemically modified papers, acetylated papers, and pure cellulose papers of different grades like No.1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 17, 20, 40, 42, etc are used as stationary phases in paper chromatography.
- What is the major difference between thin layer chromatography and paper chromatography? The major difference between TLC and paper chromatography is that the stationary phase of the paper chromatography is a cellulose paper while TLC uses a thin layer of silica or alumina supported on a flat surface.
- ¿How does temperature affect paper chromatography? Paper chromatography is a technique in chemistry that is used to separate a complex mixture of components or solutes with varying solubility and a degree of adsorption. In this technique applying a sample (dot) near one corner of the paper and the mobile phase runs throughout the paper and samples can be separated according to the affinity toward the stationary phase. Both thin layer chromatography (TLC) and paper chromatography work on the same principle.
Temperature can affect the separation of components in all chromatography types. If the temperature rises, the heat transfers further energy to the solvent-giving the molecule the power to escape from the surface of the liquid hence increases the transfer of liquid to the vapor phase.
Paper chromatography and thin-layer chromatography (TLC) has two counteracting effects of temperature first is the changes in the retention time, that is, if the temperature increases, the retention decreases, and the second one are increased temperature will reduce the elution strength of the molecule and density of the mobile phase. The temperature also affects the solubility of substances, the more the temperature, the more the solubility of the substances.
Topics about paper chromatography
Difference between TLC and Paper Chromatography
TLC and paper chromatography both are separation techniques of chromatography, which are used to separate the components or biomolecules such as carbohydrates, amino acids, and proteins. As a stationary phase, the paper chromatography uses a cellulose paper, and the separation mechanism depends on the solid-liquid adsorption.The same adsorption mechanism uses in thin layer chromatography, depending on solubility in the mobile phase the molecules or components are separated on the stationary phase. TLC uses the stationary phase as alumina, silica, and its compositions, whereas in paper chromatography, as a stationary phase paper is being used.
- Thin Layer Chromatography:TLC is another separation technique of chromatography, which works based on the solid-liquid adsorption of compounds. It has a stationary phase of silica gel or alumina and a solvent in the form of a mobile phase. TLC and paper chromatography use both to determine the sample retention factor.
- Paper Chromatography:Paper chromatography is a separation technique of chromatography that uses to separate the different compounds depends on the compound's solubility and liquid-liquid adsorption. It uses a paper as its stationary phase.
Applications of Paper Chromatography in Pharmaceutical Analysis
Paper chromatography is one of the kinds of chromatography which is used for separating complex mixtures and identifying the analytes or components. The mixture gets separated since several analytes will attract more to the stationary phase (a piece of specialized paper) and several components can be attracted to the mobile phase hence they travel with it. Paper chromatography is typically utilized as an instructing to explain the basic functions of chromatography, but it is used in some applications, let's check it out.
- Reaction monitoring.
- To ensure the control of the purity of pharmaceuticals.
- For the study of ripening and fermentation.
- For the analysis of the reaction mix in biochemical laboratories.
- To detect contaminated substances in beverages and foodstuffs.
- For the analysis of cosmetics.
- Separation and purification techniques for components.
- Forensic testing.
- Performance-enhancing drug testing.
Commonly asked questions on paper chromatography are as follows.
What industries use paper chromatography?
Paper chromatography is commonly used in the analysis of various foods as well as in the pharmaceutical industries. It is mostly used in the analysis of colors that is used in the ice-creams, sweets, jams & jellies, beverages, and other foodstuffs.
What is the principle of paper chromatography?
The paper chromatography and thin-layer chromatography (TLC) works on the same principle that is partition chromatography in which the molecules are partitioned or distributed between liquid phases.
What factors affect paper chromatography?
Many factors affect paper chromatography such as the concentration of the sample, the length of the paper, type of solvent or mobile phase used, the thickness of paper, quality of paper used, and working temperature.
Difference between paper and column chromatography
Chromatography is a significant biophysical method that allows the separation, purification, and detection of the analytes of complex mixtures for the quantitative and qualitative analysis. Paper chromatography and column chromatography both are used in the separation of components in chromatography.The key difference between paper chromatography and column chromatography is that the column chromatography in which the different solutes of a sample solution are permitted to move with the gravitational force to the absorptive column (The column is usually made of glass or plastic tube, which set vertically and filled with a stationary phase) and each component is being absorbed by the stationary phase.
Paper chromatography that uses a sheet of filter paper or blotting paper as a stationary phase, the sample can introduce as thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and the mobile phase can move up to separate the sample according to its polarity.
Advantages of TLC over Paper Chromatography
TLC is a chromatographic method of separation of the analytes or components in the mixture of samples. TLC consists of two phases, one mobile and one solid phase, in which the TCL plate acts as a stationary phase.
Paper chromatography is the types of chromatography, which are used qualitatively for the separation and identification of sample components, or analytes, that can be colored or especially pigments. It runs on a piece of paper that acts as a stationary phase on which the separation occurs. Thin-layer chromatography is parallel to paper chromatography, TLC and paper chromatography as compare with each other, The TLC has a wide range of adsorbent, depending on sample and development. After development sample can be easily separated from TLC. Thin-layer chromatography offers many advantages over paper chromatography, some of which have been mentioned here.
- Time-saving method.
- The sensitivity of detection is more in TLC.
- Rigid support.
- The option of support.
- Simple Setup.
- The amount of the sample application is in minute quantity (in microlitre).
- Strong reagents can be used for the purpose of identification.
- Choice of spray reagents.
- Higher sample throughput and lower analysis time.
- If required for spot development, the thin-layer chromatography plates can be heated.
In short, the thin layer, chromatography provides several advantages for separation than the paper chromatography.
👩🔬 If you want to know other articles similar to The Principle of Paper Chromatography: A Comprehensive Guide you can visit the HPLC BASICS
 Prinzip und Ablauf der Ionenaustauschchromatographie
Prinzip und Ablauf der Ionenaustauschchromatographie HPTLC-Chromatographie - Prinzip und Vorgehensweise
HPTLC-Chromatographie - Prinzip und Vorgehensweise HPLC-Prinzip
HPLC-PrinzipWenn Sie weitere ähnliche Artikel kennenlernen möchten The Principle of Paper Chromatography: A Comprehensive Guide können Sie die Kategorie Flüssigkeitschromatographie.
Deja una respuesta

Sie könnten interessiert sein an